Insulation plays a pivotal role in maintaining the comfort, energy efficiency, and health of your living environment. Yet, the consequences of poor insulation extend far beyond discomfort, leading to significant energy loss and various health risks. This article dives into the science behind insulation, the signs of inadequate insulation, the financial and health costs of energy loss, and the environmental implications of inefficient insulation practices. By understanding these aspects, homeowners can make informed decisions, ensuring their properties are well-insulated, energy-efficient, and safe.
The Science of Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Insulation acts as a barrier to heat flow, crucial for keeping a building warm in the winter and cool in the summer. Its effectiveness is measured in R-values, indicating the material’s resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation’s performance. Proper insulation reduces the demand for heating and cooling systems, leading to significant energy savings and a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Different types of insulation materials, including fiberglass, foam, and cellulose, offer varying degrees of effectiveness. Each type is suited to different applications, and selecting the right one is essential for maximizing energy efficiency. Innovations in insulation materials continue to improve R-values, making it easier than ever to enhance a building’s energy performance. Understanding these options allows for tailored solutions that meet specific energy efficiency goals.
Identifying Poor Insulation in Your Home
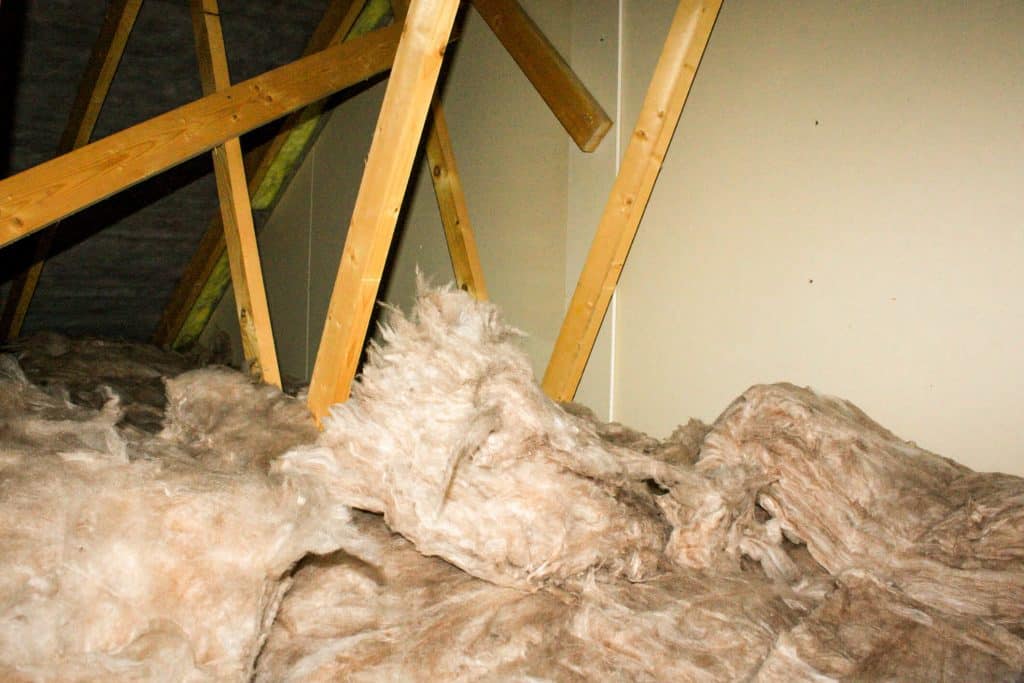

Signs of poor insulation are often subtle but telltale. Uneven temperatures between rooms, unusually high energy bills, and ice dams on the roof in winter are common indicators. These symptoms suggest that heat is escaping from or entering the home too easily, pointing to inadequate insulation. Recognizing these signs early can prevent excessive energy waste and higher costs.
Conducting a basic insulation check involves inspecting attics, walls, and floors for gaps or deteriorating insulation. For a comprehensive assessment, homeowners can opt for a professional energy audit. This evaluation pinpoints areas lacking insulation and identifies opportunities for improving overall energy efficiency. Addressing these issues can lead to significant improvements in comfort and energy savings.
The Direct Costs of Energy Loss

Energy loss due to poor insulation directly impacts homeowners’ wallets. Inefficient thermal barriers allow heat to escape during winter and enter during summer, leading to higher utility bills. Studies show that upgrading insulation can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 50%, offering substantial long-term savings. This financial benefit underscores the importance of investing in high-quality insulation.
The comparison of energy costs between well-insulated and poorly insulated homes reveals the economic impact of insulation decisions. Case studies highlight that the initial investment in better insulation pays off through reduced energy bills and increased property values. Moreover, many regions offer incentives for energy-efficient upgrades, further reducing the cost of insulation improvements. These financial advantages make a compelling case for prioritizing insulation in any home.
Health Risks

Inadequate insulation contributes to several health risks, primarily through the promotion of damp and moldy conditions. Moisture can accumulate in poorly insulated walls and ceilings, creating an ideal environment for mold growth. Exposure to mold spores is linked to respiratory problems, allergies, and other health issues, emphasizing the need for effective insulation as a preventative measure.
Beyond mold, poor insulation can lead to drafts and cold spots within a home, contributing to discomfort and exacerbating conditions such as arthritis. Ensuring a consistent indoor temperature through proper insulation enhances comfort and supports overall health and well-being. Addressing insulation flaws can significantly reduce the risk of health problems associated with cold, damp living conditions.
Environmental Impacts

The environmental repercussions of inefficient insulation extend well beyond individual homes, contributing significantly to global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Buildings with poor insulation require more energy to maintain comfortable temperatures, leading to increased use of fossil fuels and higher carbon footprints. This unnecessary energy expenditure exacerbates climate change, making it imperative to consider the environmental impact of your insulation choices.
By improving insulation, you can drastically reduce your home’s energy demand, thereby diminishing the reliance on non-renewable energy sources. Such enhancements contribute to more sustainable and environmentally friendly building practices and align with global efforts to combat climate change. Upgraded insulation acts as a key player in the broader narrative of environmental conservation, showcasing how individual choices can have a collective positive impact on the planet.
Technological Advances in Insulation Materials

Recent years have seen significant advancements in insulation technology, introducing materials that offer superior energy efficiency, durability, and health benefits. For instance, aerogel, with its exceptional thermal resistance, represents a leap forward in insulation technology. These materials are more effective at preventing heat flow and lighter and thinner, providing solutions for spaces where traditional insulation might not be feasible.
Moreover, eco-friendly insulation options, such as sheep’s wool and recycled denim, are gaining popularity for their minimal environmental impact and non-toxic properties. These innovations enhance a building’s energy performance and contribute to a healthier indoor environment by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals often found in traditional insulation. As this trend moves forward, the development and adoption of advanced insulation materials will be crucial in achieving energy efficiency and sustainability goals.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations

Building codes and regulations around insulation are evolving to address the growing concerns over energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. These laws mandate minimum insulation standards for new constructions and renovations, ensuring that buildings meet specific energy performance criteria. Compliance with these regulations is not just about legal adherence; it significantly contributes to energy conservation and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding and implementing these requirements is essential for any construction or renovation project.
Governments worldwide are also offering incentives and rebates for homeowners and builders who upgrade their insulation to exceed standard requirements. These programs aim to encourage the adoption of energy-efficient practices by offsetting some of the upfront costs associated with high-performance insulation. Staying informed about these opportunities can provide financial benefits while promoting a shift towards more sustainable building practices. As regulations become stricter and incentives more enticing, the trend towards better insulation is expected to grow, benefiting both the environment and the economy.
Make Comfort and Sustainability Your Priority
Understanding the critical role of insulation underscores the necessity for immediate action. By prioritizing upgrades in insulation, not only do you enhance your living conditions, but you also take a significant step toward energy conservation and environmental protection. Let this serve as a prompt to evaluate and improve your insulation, fostering a sustainable future while reaping the benefits of reduced energy costs and a healthier living environment. The time to act is now—make the choice for a better insulated, more efficient, and environmentally conscious home.


